Blockchain has been one of the biggest disruptors since the emergence of the internet. It took world commerce to the next level by introducing cryptocurrency, the most phenomenal use-case of blockchain, and made the fintech sector reach new heights. The primary reason for accomplishing new heights is blockchain’s immutable, transparent, and highly secure nature. So what exactly is a blockchain? How do the transactions work? What is the role of contracts in the process? What is a decentralized application? To all such questions wandering over your mind, this blog is the key. Get ready to unveil the answers!
What is Blockchain?
A blockchain is a distributed and transparent database, and the different nodes present in the network share the database to process it together. The technology is a cryptographic chain that allows anyone to connect seamlessly in a peer-to-peer approach without intermediaries. It collects information in groups and stores them in blocks and gets linked with previous blocks in the chain, thereby referring to the blockchain. The transactions in the network are stored in a trustless manner, and the nodes will examine each block and add it to the chain.
Bitcoin holds the pride of being the first cryptocurrency globally, published by the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin’s whitepaper provides a remedy to the double-spend limitation and brings in the concept of peer-to-peer payments.
The Evolution of Blockchain
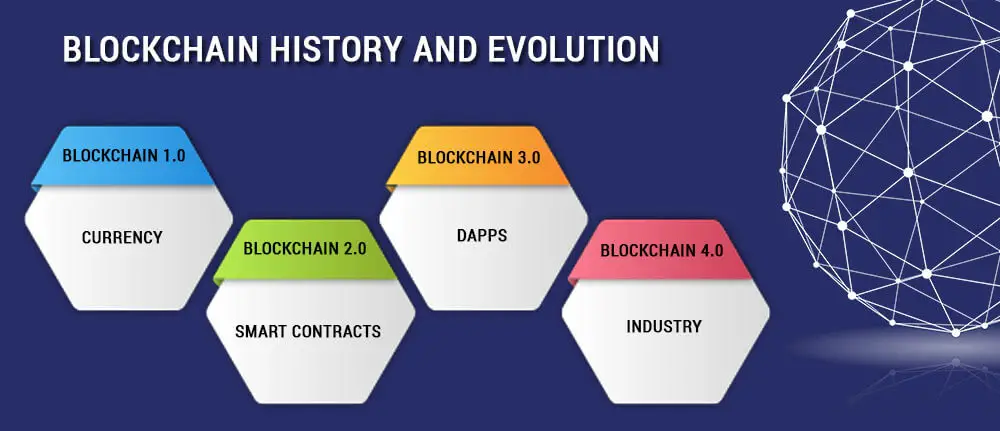
We are currently using the third generation of blockchain. Blockchain 1.0 and Blockchain 2.0 are often referred to as the starting phases. Each phase has its own limitations, and each successive stage solves those deficiencies to bestow a frictionless experience. Some of the serious challenges of the first and second generations include scalability and interoperability. Blockchain 3.0 protocols eliminate these issues with zero knowledge roll-up mechanisms, new consensus algorithms, and brand-new bridging solutions to teleport an asset from one to another.
This assorted range of solutions offered by blockchain 3.0 ecosystems has started to capture people’s attention and make them use cryptocurrencies for their day-to-day needs. Network congestion and high gas fees are serious issues that make users step back from making a transaction. This is because, even for a small transaction, they have to pay higher transaction fees. Bridges and layer two solutions greatly help improve the scalability of the networks, which can accept more than 1000 transactions per second.
How Do Transactions Occur in the Blockchain?
On getting back to Nakamoto’s whitepaper, it is clear that all crypto-asset transactions are trustless entities, which eradicates the need for third parties to complete the transactions. For instance, in the traditional financial system, if you pay your friend Rs. 500 through internet banking, the bank has to approve the transaction, and third parties will be present to validate the transaction and approve it to reach the recipient. This presence of intermediaries will ultimately increase the cost and time, which is directly reflected in the transaction fee.
It solves this problem with trustless and peer-to-peer activity, which removes intermediaries. The nodes will validate each transaction in the network and add it to the blockchain via computational proofs and hashes. This enables the networks to make it an ultra-fast transaction at an affordable transaction fee.
What are Contracts in Blockchain?
The blockchain 3.0 protocols have use-cases beyond peer-to-peer transactions. It allows developers to build decentralized applications (dApps) on top of the network with high speed and robust security. Any idea on how this dApp building became possible? Cool, Smart Contract is the answer!
Though Bitcoin is the first cryptocurrency and the first blockchain, it does not have wider options for other purposes than financial transactions. Bitcoin is used only as an asset to store value or purchase goods/services. On the flip side, Ethereum is the third-gen blockchain framework that supports smart contracts. The use of smart contracts brings in a plethora of use cases from dApps, games, NFTs, to much more.
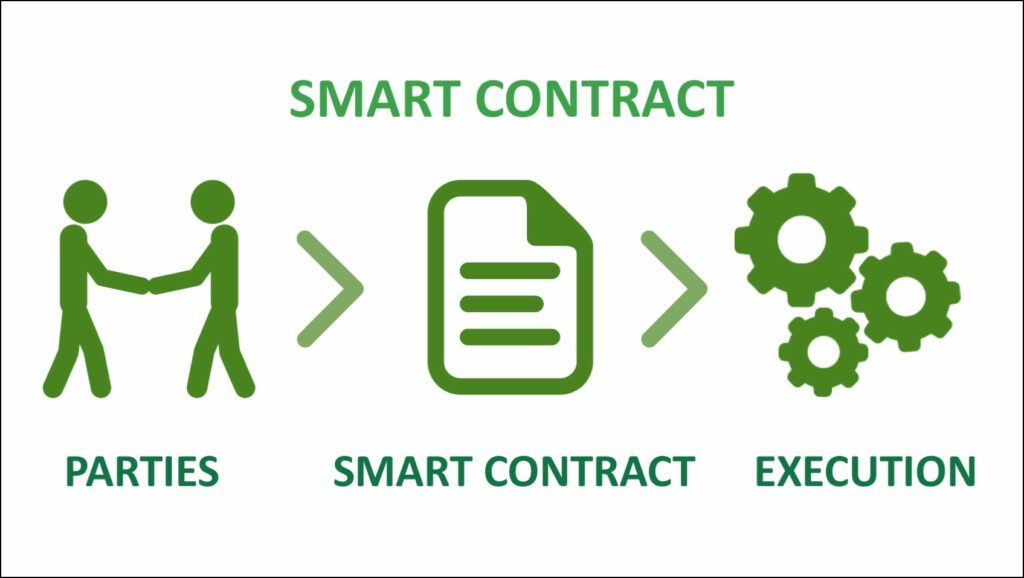
A smart contract is a set of codes created by developers to make a decentralized application a trustless ecosystem without the involvement of financial bodies or intermediaries. No one can change these rules once the smart contracts are deployed. It automates the process when both parties fulfill their side of the agreement and makes it a trustless ecosystem.
What is a Decentralized Application on Blockchain?
Decentralized applications are the hottest products in the Blockchain 3.0 protocols. The use of smart contracts will enable technologists to build their own dApps on the network. For instance, they can develop a lending and borrowing application using crypto assets. The smart contracts will function as escrow and ensure both the lender and receiver meet the required agreements. It is almost impossible to cheat or involved in any fraudulent activities as smart contracts will have complete responsibility, from accepting the collateral to disbursing the loan.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What are the different types of blockchains available?
The various types include,
Public Blockchain: It is the basic ecosystem where anyone can use the database to see the transactions in the network. Bitcoin & Ethereum fall under this category.
Permissioned Blockchain: Consortium blockchain is the other name for permission blockchain. Here, the database is only available to the nodes in the network. Imagine if a centralized entity were developing a blockchain for the rest of the users worldwide. Then it would be a permissioned blockchain.
Private Blockchain: This blockchain variant is also not transparent and does not show the databases to its users. It might have some information available to the workforce, but only C-suite executives can access all the private information.
Hybrid Blockchain: This is recognized as the future of blockchain protocols as it amalgamates the characteristics of both public and private blockchains.
Q. What is Proof of Stake?
It is an alternative consensus mechanism to proof of work. Here, users have to stake the native cryptocurrency to validate transactions in the network. For each correct validation, they will earn a reward, and if the validation is wrong, they may lose some assets.
Q. Why are gas fees high in some of the prominent networks?
The traffic on the network will be high in the prominent networks. Their scaling mechanisms will enable only 15-20 transactions per second. This makes others wait in the queue to confirm their transaction. To make the validators quickly confirm the transaction, users give high charges as incentives. The higher the pay, the higher the chances to swiftly confirm the transaction.
Wrapping Up
Thus, blockchain is a boon to technologists, and it has started to revolutionize a wide range of industries apart from fintech. It has become a buzzword on the tongues of every individual. This is because it helps businesses scale more efficiently, accurately, cheaply, and with fewer middlemen. We are equally as excited as you to know how blockchain will transform the existing world within the next ten years.
You can also follow us for instant tech news at Google News or for tips and tricks, smartphones & gadgets reviews, join GadgetsToUse Telegram Group or for the latest review videos subscribe GadgetsToUse Youtube Channel.