Quick Answer
- If it shows LTE and only a single band, then there can be three possible reasons- either your phone doesn’t support carrier aggregation, OR the carrier hasn’t enabled it for your area, OR the aggregation supported network band is not available in your location.
- If you don’t see any useful leads and at the same time can’t find the LTE or Carrier Aggregation feature in settings, the phone likely doesn’t support it in the first place.
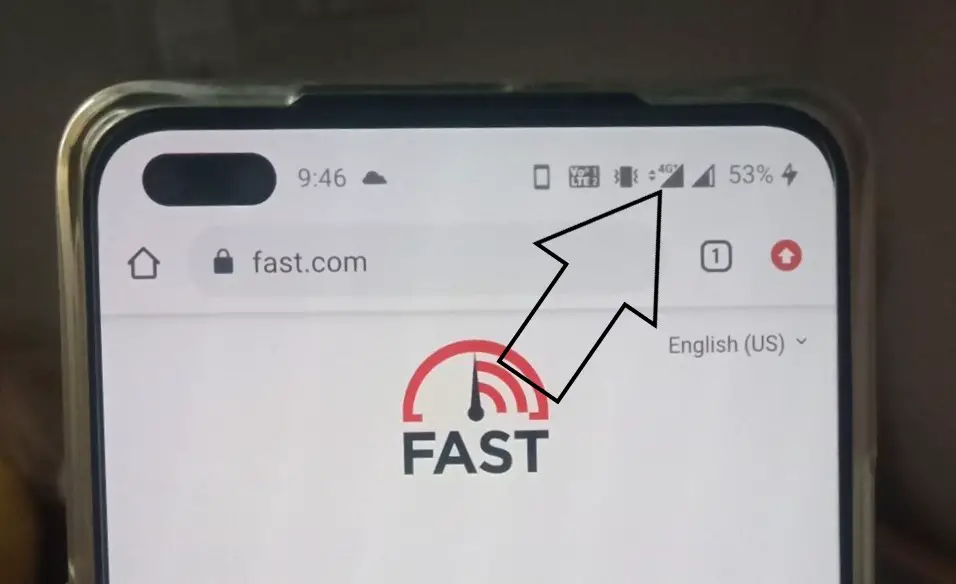
- If your is actively using Carrier Aggregation at a given moment, the 4G or LTE icon on the status bar will change to 4G+, LTE+, or LTE-A, indicating LTE-Advanced network.
Carrier Aggregation in smartphones helps offer more bandwidth and faster data speeds by combining different network bands. It’s usually present on most modern mid and high-priced smartphones and could be a deal-breaker for people buying a smartphone. In this article, let’s look at some quick ways to check if your phone supports carrier aggregation for Android and iOS.
Related | Check Phone Network Signal Quality on Android and iPhone
How to Check if Your Phone Supports Carrier Aggregation
Your phone uses different bands, i.e., a range of frequencies, for communicating with the cell towers. Previously, the phones could only connect to one band at a time, causing sluggish data speeds even with a high network signal strength. However, things have changed with the introduction of Carrier Aggregation.
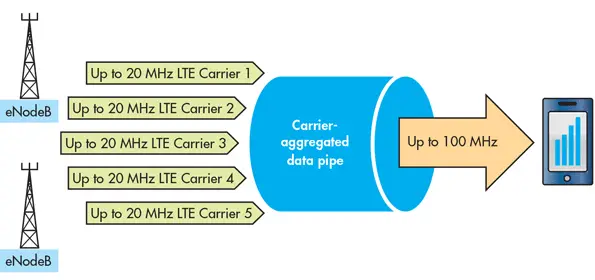
For starters, Carrier Aggregation (CA) is a technology that combines multiple frequency bands. It allows combining two or more LTE carriers into a single data channel to increase the network capacity. This helps offer better network connectivity and data speeds.
In 4G, carrier aggregation is adopted as part of LTE-Advanced to aggregate a maximum of five component carriers of 1.4, 3, 5, 10, 15, or 20 MHz to increase bandwidth. Phones with LTE-Advanced can achieve a maximum aggregated bandwidth of 100MHz.
Carrier Aggregation Support
Whether your phone will support carrier aggregation or not depends on your phone and network operator. Indian telcos, including Jio, Airtel, and Vodafone Idea, have implemented CA in most of its circles. Jio has enabled it on all bands (band 3, 5 & 40), while Airtel supports it on Band 3 and 40.
Phones powered by Qualcomm chipset having an X5 modem or later have hardware support for Carrier Aggregation. Several phones with Mediatek, Kirin, and Exynos chipsets also support aggregation for the Indian telecom operators.
Unfortunately, despite having hardware support for CA, some smartphone brands may choose not to enable it at the software-level. For instance, several phones from Realme don’t support CA even though they have supported SoCs.
Benefits of Carrier Aggregation
- Higher and consistent data speeds.
- Lower ping- avoid micro lag in online gaming.
- Reduce buffering while streaming high-quality videos.
- Avoid excess battery drain caused by buffering and network oscillation issues.
Check Carrier Aggregation Support on Android Phones
1. Through Status Bar & Settings
If your is actively using Carrier Aggregation at a given moment, the 4G or LTE icon on the status bar will change to 4G+, LTE+, or LTE-A, indicating LTE-Advanced network. However, the feature needs to be enabled manually in the settings.
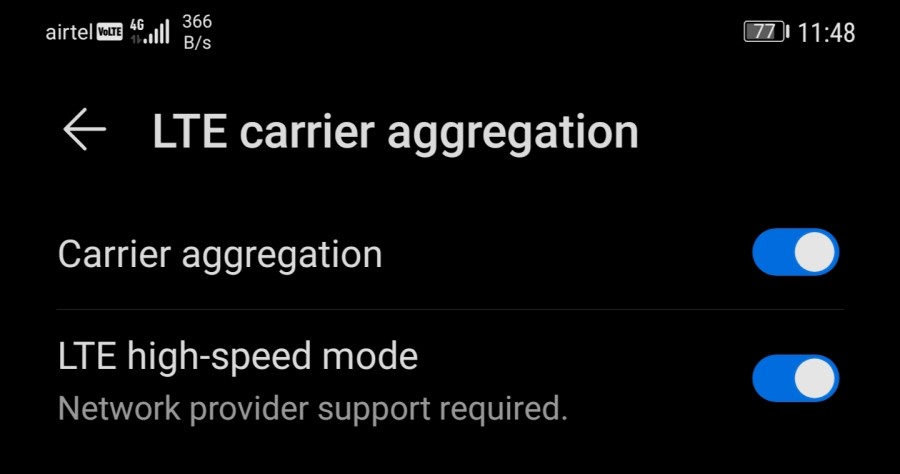
To check for it, open Settings on your Android phone. Here, use the search bar at the top to look for “Carrier Aggregation” or “LTE Carrier Aggregation.” The option is usually present in Mobile Network Settings, System Settings, or Developer Options.
Note: Carrier Aggregation will work only if your network operator supports it.
2. Lookup on the Internet
Smartphone companies usually mention the Carrier Aggregation in their specification sheet. However, if you don’t seem to find it on the manufacturer’s website, a simple Google search will likely clear up the confusion.
If you don’t see any useful leads and at the same time can’t find the LTE or Carrier Aggregation feature in settings, the phone likely doesn’t support it in the first place. However, there’s one more way to find it, given below.
3. Using NetMonster
The NetMonster app gives another way to check whether your Android phone supports Carrier Aggregation or not. You can check the same as follows:
- Install the NetMonster app on your phone from Google Play Store.
- Open the app and allow the necessary permissions.
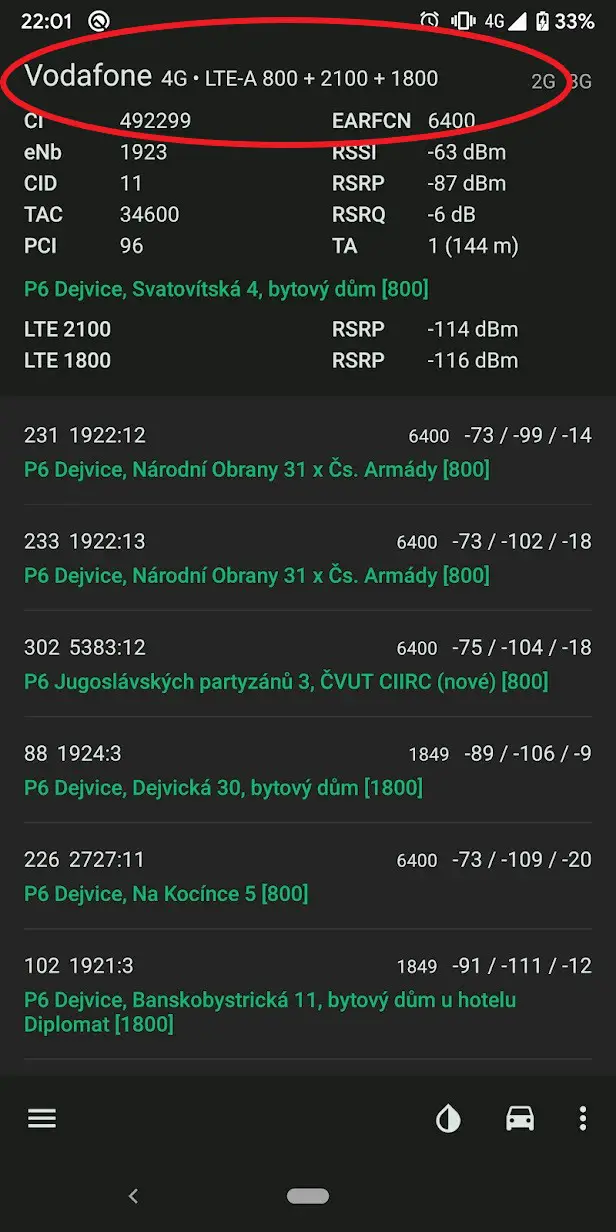
- On the top, you’ll see the bands your phone is currently using.
- If you see “LTE-A,” followed by multiple bands with a “+” sign, then your phone is currently using Carrier Aggregation to aggregate different bands together.
If it shows LTE and only a single band, then there can be three possible reasons- either your phone doesn’t support carrier aggregation, OR the carrier hasn’t enabled it for your area, OR the aggregation supported network band is not available in your location.
Check Carrier Aggregation Support on iPhone (iOS)
All iPhones starting iPhone 6s (including iPhone 6s, iPhone 6s Plus, iPhone 7, iPhone 7 Plus, iPhone 8, iPhone 8 Plus, iPhone X, iPhone XS, iPhone XS Max, iPhone XR, iPhone 11-series, and iPhone 12-series) support Carrier Aggregation.
However, unlike Android, you cannot check whether the Carrier Aggregation is actively being used on iPhone through the notification bar or a third-party app. Instead, you can check for it in the field test menu.
Using Field Test Menu
- Open the Dialer app on your iPhone.
- Dial *3001#12345#* and press the Call button. You will enter in Field Test Mode.
- Here, click the List icon at the right.
- Scroll down and click on Serving Cell Info under LTE.
- Here, the “freq band indicator” shows the primary band your phone is using.
- Then, go back and click on CA Status.
- If you see more than one component carrier, like Component Carrier 0, Component Carrier 1, and so on, then your iPhone is currently using Carrier Aggregation.
The index value 1 indicates that this is the 1st additional carrier (also known as the component carrier) your iPhone uses alongside the primary carrier shown above. At the same time, dl_rf_band with value 3 (say) indicates that your iPhone is also using LTE Band 3 in addition to Band 28.
Wrapping Up
These were some quick ways to check for Carrier Aggregation support on your Android device or iPhone. Let me know if your phone supports CA in the comments below. Also, do share if you notice any difference in speeds or overall connectivity when your phone is connected to 4G+ or LTE+. Stay tuned for more such articles.
Also, read- What is GLONASS And How It Is Different From GPS?
You can also follow us for instant tech news at Google News or for tips and tricks, smartphones & gadgets reviews, join GadgetsToUse Telegram Group or for the latest review videos subscribe GadgetsToUse Youtube Channel.