Quick Answer
- To explain it further, it will work just like UPI in an online payment system, which means users will have the choice to buy and transact from their choice of app, and they will have the liberty to choose from all sellers and vice versa sellers too.
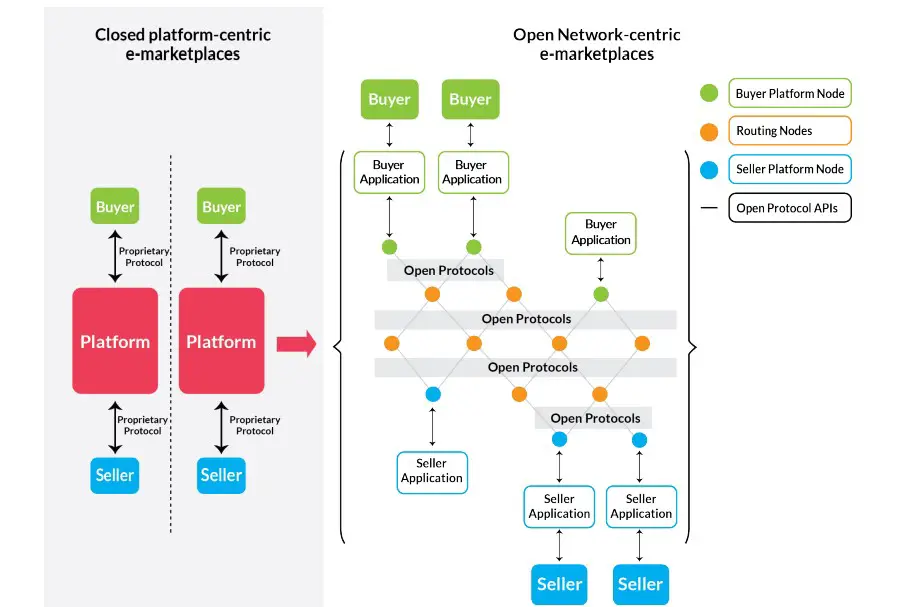
- Like the UPI, the ONDC will develop an open network designed in such a way that lets all e-com apps and platforms connect with each other in the same way that the UPI allows all payment apps to transfer money seamlessly.
- In this article, we will try to answer some queries related to ONDC, such as what it is, how it will work, and what benefits it will have for buyers and sellers.
India recently announced Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) to democratize the e-commerce space in India and end the dominance of US-based big players like Amazon. The ONDC will be a platform that will allow buyers and sellers to connect and transact with each other regardless of which shopping app they’re using.
The government has already launched a pilot phase of this ONDC in five cities back in the last week of April. This free-to-use online system will provide an open platform for buying and selling goods and services and let local retailers participate in the e-com race.
In this article, we will try to answer some queries related to ONDC, such as what it is, how it will work, and what benefits it will have for buyers and sellers.
ONDC FAQs
1. What is ONDC?
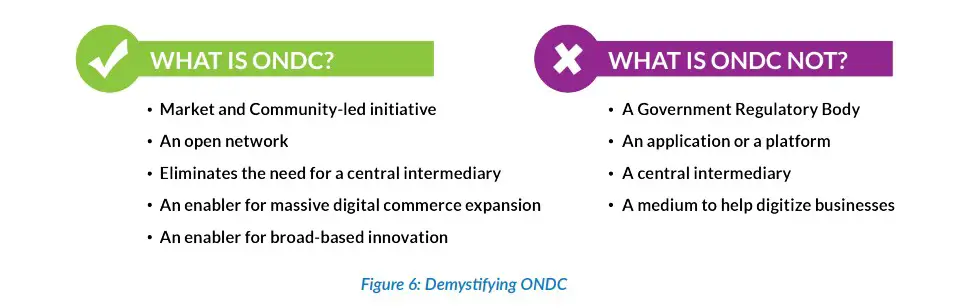
Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) is an open-source network that will provide a common platform for all buyers and sellers to transact and order goods and services from their preferred place. The open network will take on big e-commerce players like Amazon and Walmart-owned Flipkart in India. To explain it further, it will work just like UPI in an online payment system, which means users will have the choice to buy and transact from their choice of app, and they will have the liberty to choose from all sellers and vice versa sellers too.
2. What are ONDC features?
ONDC is just like the UPI of e-commerce. It will democratize online shopping, making it an open network from the earlier platform-centric model.
Following are some features of ONDC:
- It will have an open protocol for all buyers and sellers.
- Consumers will have more choices to buying a product.
- Local merchants will be able to make their online presence and build credit history and a consumer base.
- ONDC will make sure the privacy of data in the network remains confidential.
3. How will ONDC work in India?
ONDC will ensure that buyers and sellers use the same platform or app for all online business transactions. Like the UPI, the ONDC will develop an open network designed in such a way that lets all e-com apps and platforms connect with each other in the same way that the UPI allows all payment apps to transfer money seamlessly. ONDC network will also make small retailers online.
4. How will ONDC affect Amazon and Flipkart in India?
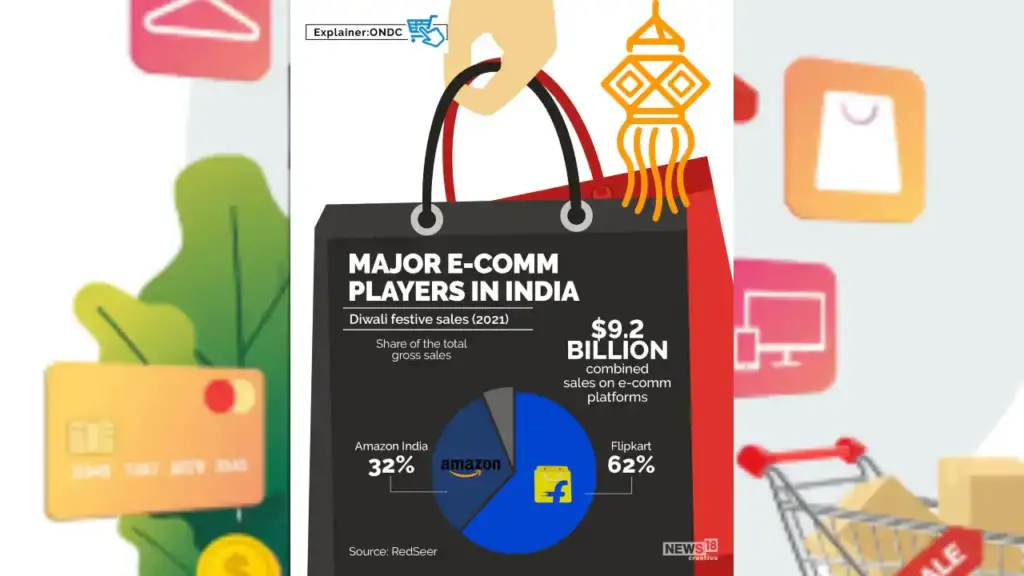
Currently, the e-com space in India is platform-centric, and it is dominated by Amazon and Flipkart. ONDC will enable more local sellers to be digitally available so the buyers will have more choices other than the sellers listed on Amazon and Flipkart. Also, buyers will have the liberty to do the transaction using an app through an open network.
This will give a tough competition to Amazon and Flipkart’s sellers, and also, although their technology will be used by users, they may or may not receive all the orders.
5. What are the benefits of ONDC for buyers?
Buyers will have the following benefits when ONDC comes into action:
- They will have access to more sellers and, therefore, have more choices.
- Customers will receive better services and faster deliveries due to local retailers.
- Overall better customer experience because of transparency in costs and delivery.
6. What are the benefits of ONDC for sellers?
Sellers will also be benefitted from this initiative. Following are some benefits:
- Will have access to more customers.
- Their product discoverability will be better.
- The cost of doing business will be lower.
- More options for services like logistics.
7. How buyers and sellers can join ONDC?
The government has launched a pilot of this program in select cities like Delhi NCR, Bengaluru, Bhopal, Shillong, and Coimbatore. However, the Department for Promoting Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) from the Ministry of Commerce and Industry is currently building this open network.
Soon a private sector non-profit organization will be set up to gear up for its faster roll-out. Once the network is ready, local retailers and other established businesses will have the option to opt in and then buyers will also have the access to it.
8. How will ONDC help small businesses and retailers?
ONDC will help millions of small businesses go digital. Recently, these SMEs have suffered during the COVID-19 pandemic, and this is a great opportunity as well as a future-proof thing for these vendors. Once they go online, they will be able to list their products or services. Then these small businesses will be discovered on e-com platforms. Consumers searching for a product will see these local sellers and buy from them for faster delivery.
9. What are the targets ONDC is aspiring for?
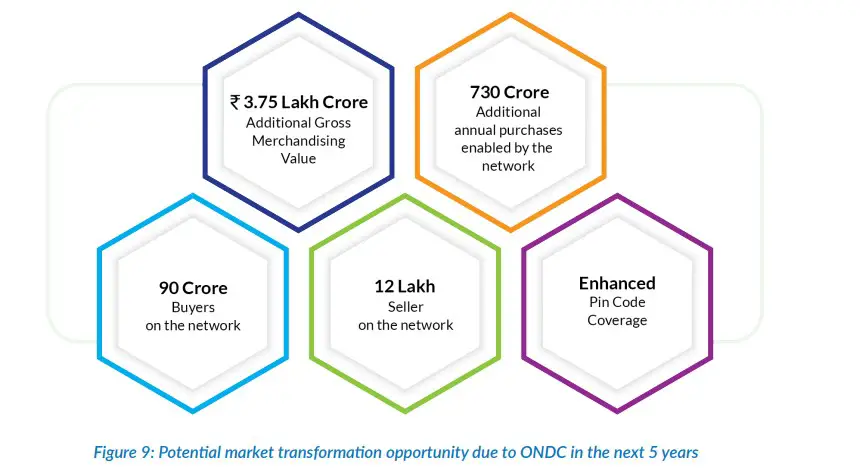
ONDC is aiming to onboard buyers and sellers from every pin code in India. The government aspires to bring 300 million shoppers and 30 million sellers onto the ONDC network via all existing platforms by the end of 2024 and to further increase the numbers in the next five years.
10. Will ONDC be a standalone app or website?
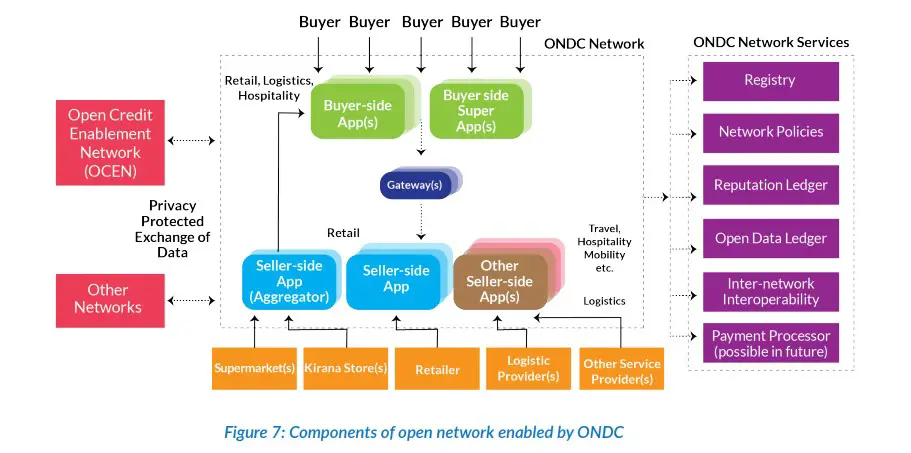
ONDC is an open network that will provide both the buyers and sellers to use the same platform to conduct a business transaction. Basically, e-comp portals such as Amazon, Flipkart, and Zomato will have to join the platform in order to be available there.
To be specific, ONDC is neither an aggregator app nor a hosting platform. All existing e-com apps can voluntarily choose to be a part of the ONDC network. The onboarding of sellers and buyers and their management will continue to be inside the network-enabled apps.
11. Is ONDC a government organization?
ONDC is a company with a shareholding of banks and financial institutions from the private and public sectors. The institutions investing in ONDC include HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, Axis Bank, SBI, Bank of Baroda, PNB, NABARD, SIDBI, Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), National Stock Exchange (NSE), National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), etc.
12. Who all are in the advisory council of ONDC?
The government has made an advisory council for ONDC. The council includes Anil Agarwal – Additional Secretary, DPIIT; R.S. Sharma – CEO of National Health Authority; Nandan M. Nilekani, non-executive chairman of Infosys; Adil Zainulbhai – Chairman, Quality Council of India; Anjali Bansal – Founder, Avaana Capital among others.
This was all about the ONDC network, which is still work-in-progress. Once the network is ready to be implemented, we’ll have more clarity on how things will actually work. Stay tuned to this page, for all the upcoming updates.
You can also follow us for instant tech news at Google News or for tips and tricks, smartphones & gadgets reviews, join GadgetsToUse Telegram Group, or for the latest review videos, subscribe GadgetsToUse YouTube Channel.