Quick Answer
- It senses the magnetic fields, both the magnitude (strength) and the direction of the field to detect your exact position in the coordinate space.
- An accelerometer is a MEMS-based circuit that senses or measures the forces of acceleration caused by the gravity of movement or tilting action.
- The altitude data is used along with other data measured by the watch to make sense of the conditions and provide you with the necessary information.
Apart from the basic hardware required to run, a smartwatch packs several important sensors to track your sleep, health and activity, stress, gestures, position, and more. This includes a gyroscope, accelerometer, GPS, heart rate sensor, and whatnot. In this article, we’ll explore all such sensors present in a smartwatch and their advantages and disadvantages.
Everything About Sensors Present Inside a Smartwatch
A 34-year-old man from Yamuna Nagar, Haryana, complained about low energy levels and chest pain. In a normal situation, anyone would probably take a rest to feel better – but he had an Apple Watch with him. He immediately used the ECG sensor, which detected irregularities and advised for medical help, and it was later revealed he had 99% blockage in his arteries.
This only shows how much wearable tech has evolved. What meets the eye are the fancy aesthetics, but deep down, the sensors are what makes them revolutionary. Here are some of the important sensors you’ll find inside smartwatches in the market and how they work.
Before we start, note that not all sensors are present on all watches. It depends on the watch’s price, target audience, and what the manufacturer intends to do. You can check what sensors a smartwatch has on the manufacturer’s website, product listing page, or user manual.
1. Accelerometer
Most fitness bands and wearables fundamentally operate on accelerometers. Accelerometers are sensors that track the movements of your body by counting the number of steps you have taken throughout a period.
At the same time, this sensor also tracks your sleep. The sensor tracks your movements during sleep. It then provides information to learn more about your sleeping patterns and effectively improve your sleeping habits.
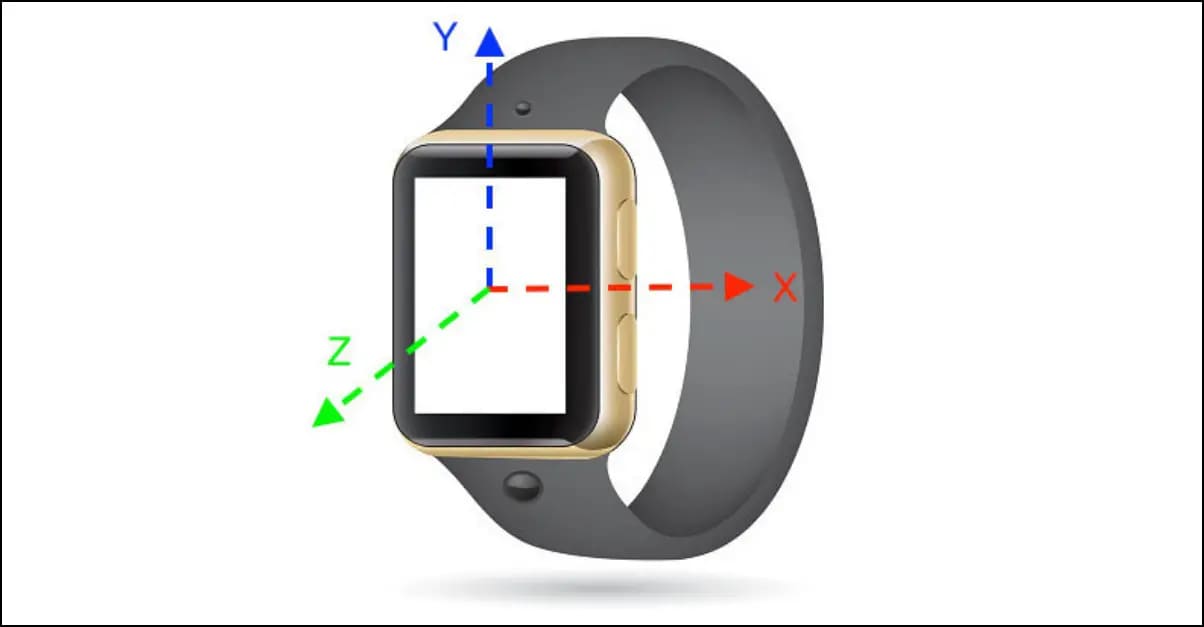
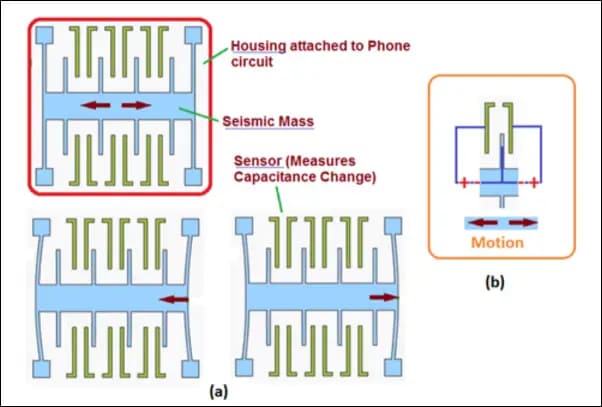
An accelerometer is a MEMS-based circuit that senses or measures the forces of acceleration caused by the gravity of movement or tilting action. It can measure the speed of acceleration or movement of the attached device. It can measure movement across the X, Y, and Z axis.
The only disadvantage is the questionable accuracy unless you use a decent-quality wearable device. According to research, sleep trackers are only found to be accurate 78% of the time. And when it comes to estimating how long it took for people to fall asleep, the accuracy dropped to a mere 38%.
2. Gyroscope
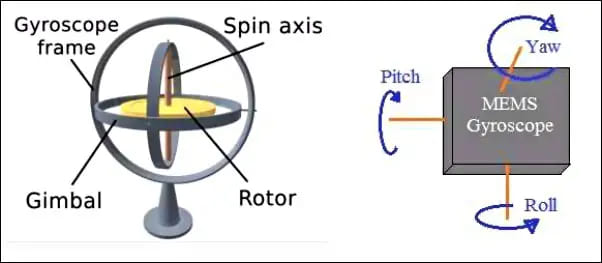
The Gyroscope sensor in a smartwatch measures the angular velocity. This means it goes beyond detecting linear motion and considers all your other movements too. The 3-axis gyroscope and 3-axis accelerometer sensors combine to perform a 6-degree motion tracking system.
The two sensors track body movements, gravity, and speed to detect motion and gestures. This is used to detect motion and track them accurately. Gyroscopes are quite helpful when it comes to differentiating one activity from another.
For example, most activity detection features on your smartwatch use the gyroscope to detect your activity and then identify whether you are jogging or running. If you’ve ever wondered how your watch does not detect just your hand motion as activity, it is because of the Gyroscope.
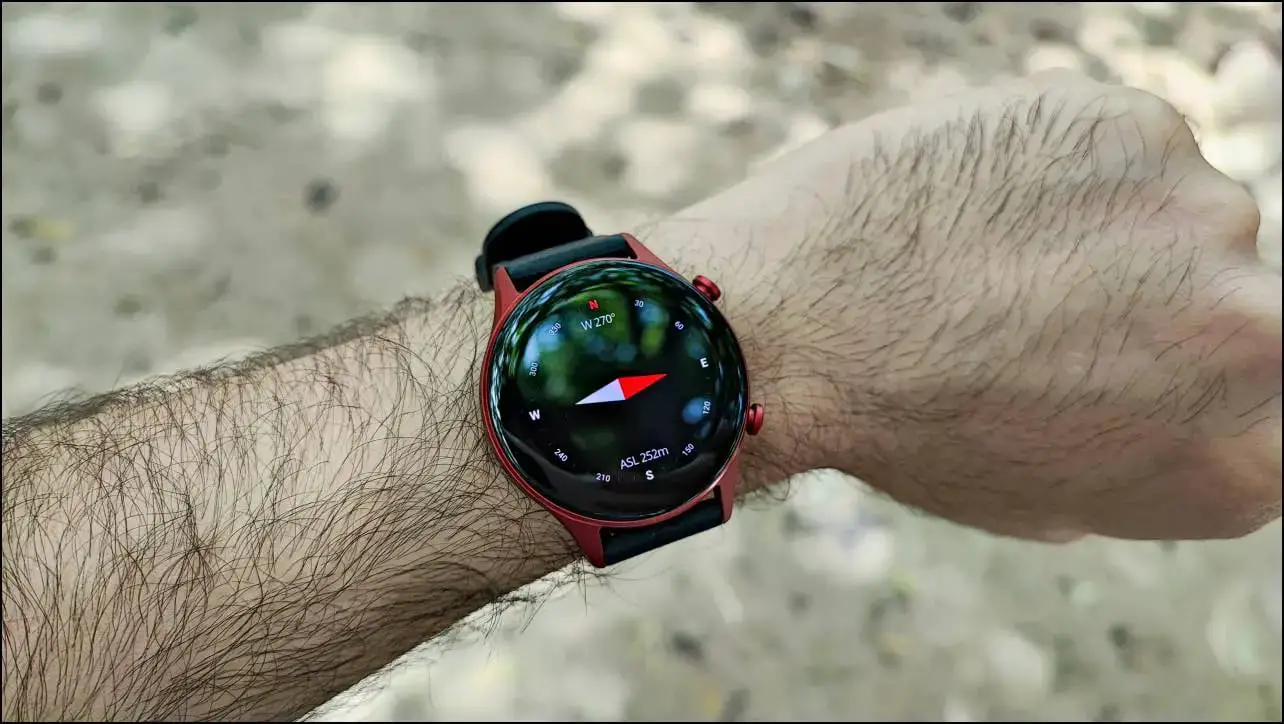
3. Magnetometer or Compass
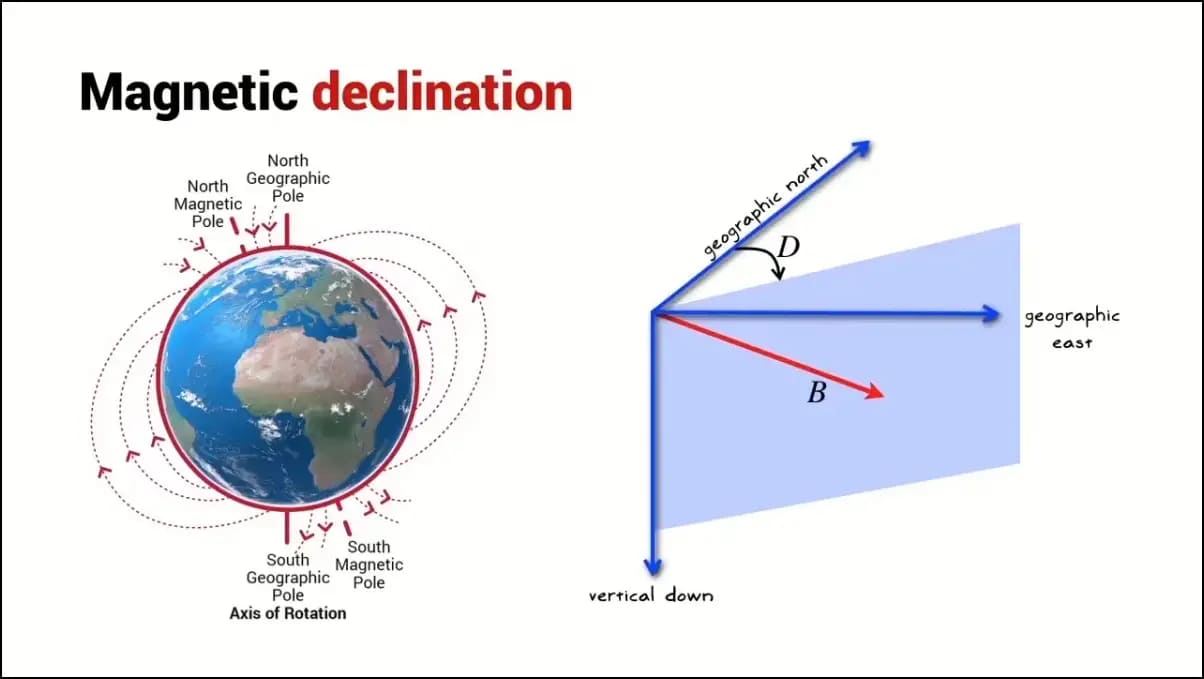
A magnetometer is nothing but another name for a compass. It works with GPS coordinates to determine the exact location and direction in which you’re standing.
It senses the magnetic fields, both the magnitude (strength) and the direction of the field to detect your exact position in the coordinate space.
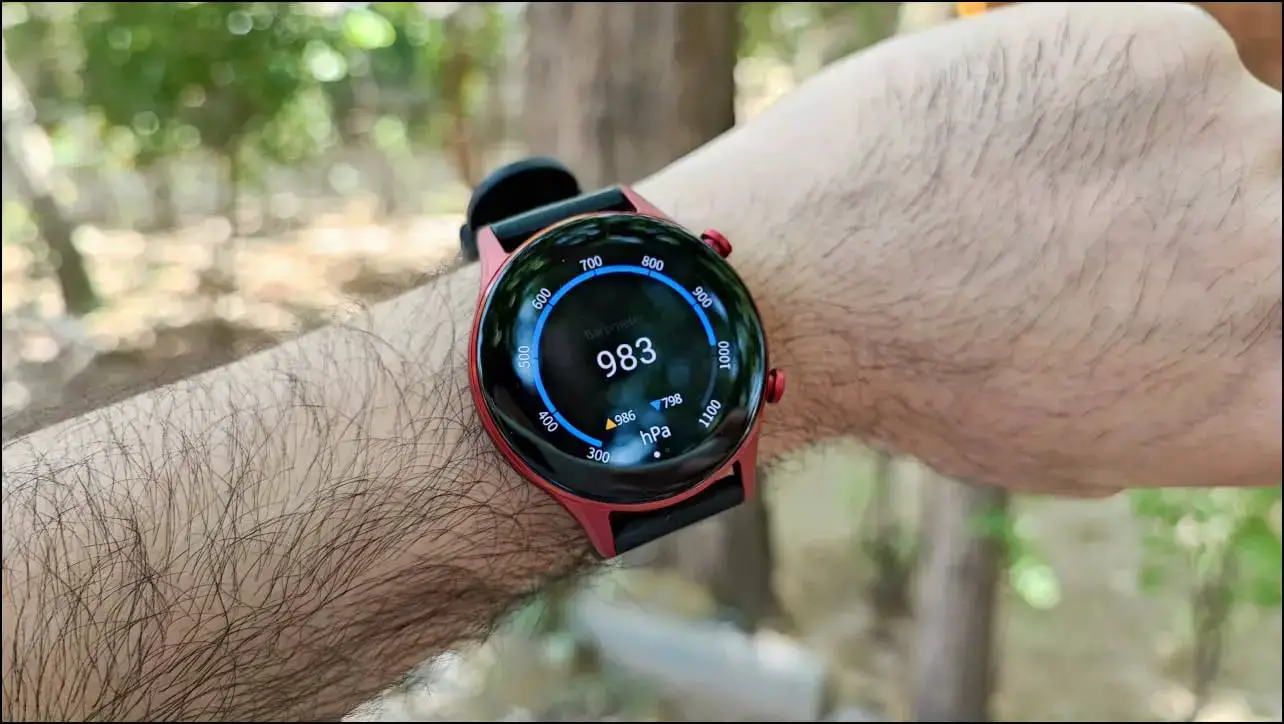
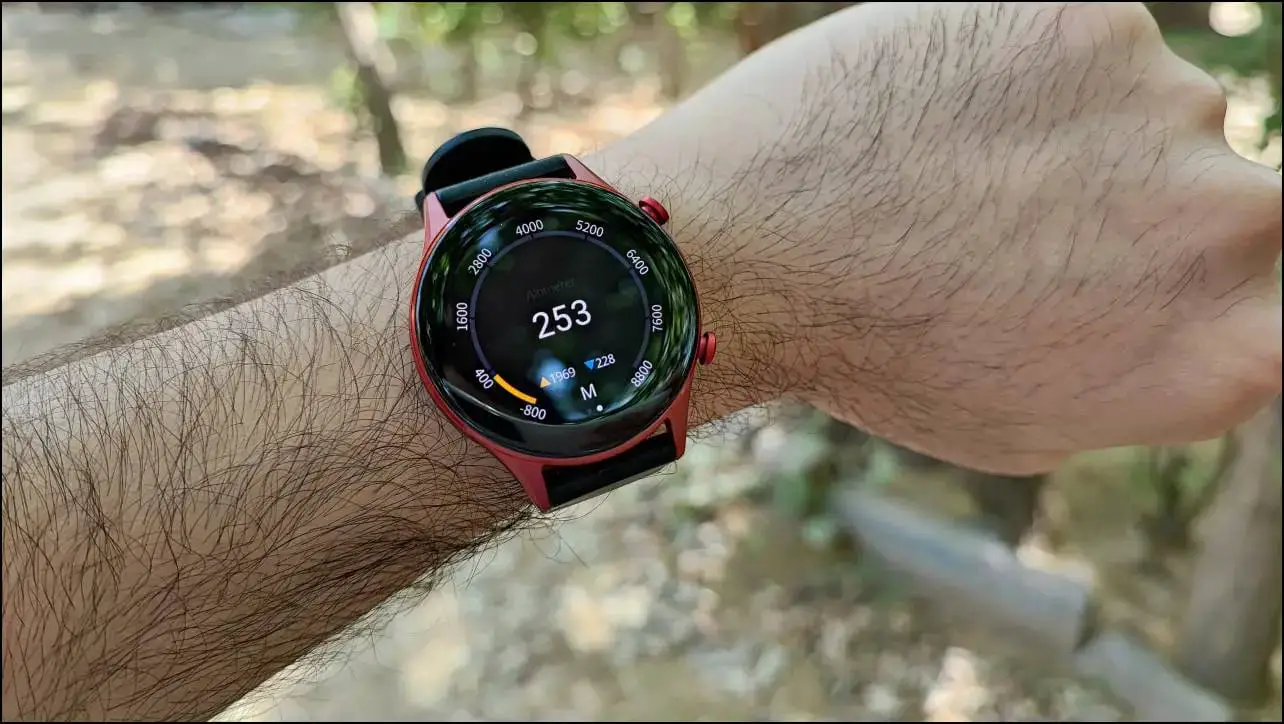
4. Barometric Pressure Sensor
Barometric pressure sensors are mainly used to detect your altitude with the smartwatch. This data is quite helpful during activities like hiking and mountain climbing.
The altitude data is used along with other data measured by the watch to make sense of the conditions and provide you with the necessary information. For example, devices can use this sensor to determine if your SpO2 levels decrease as you move to higher altitudes.
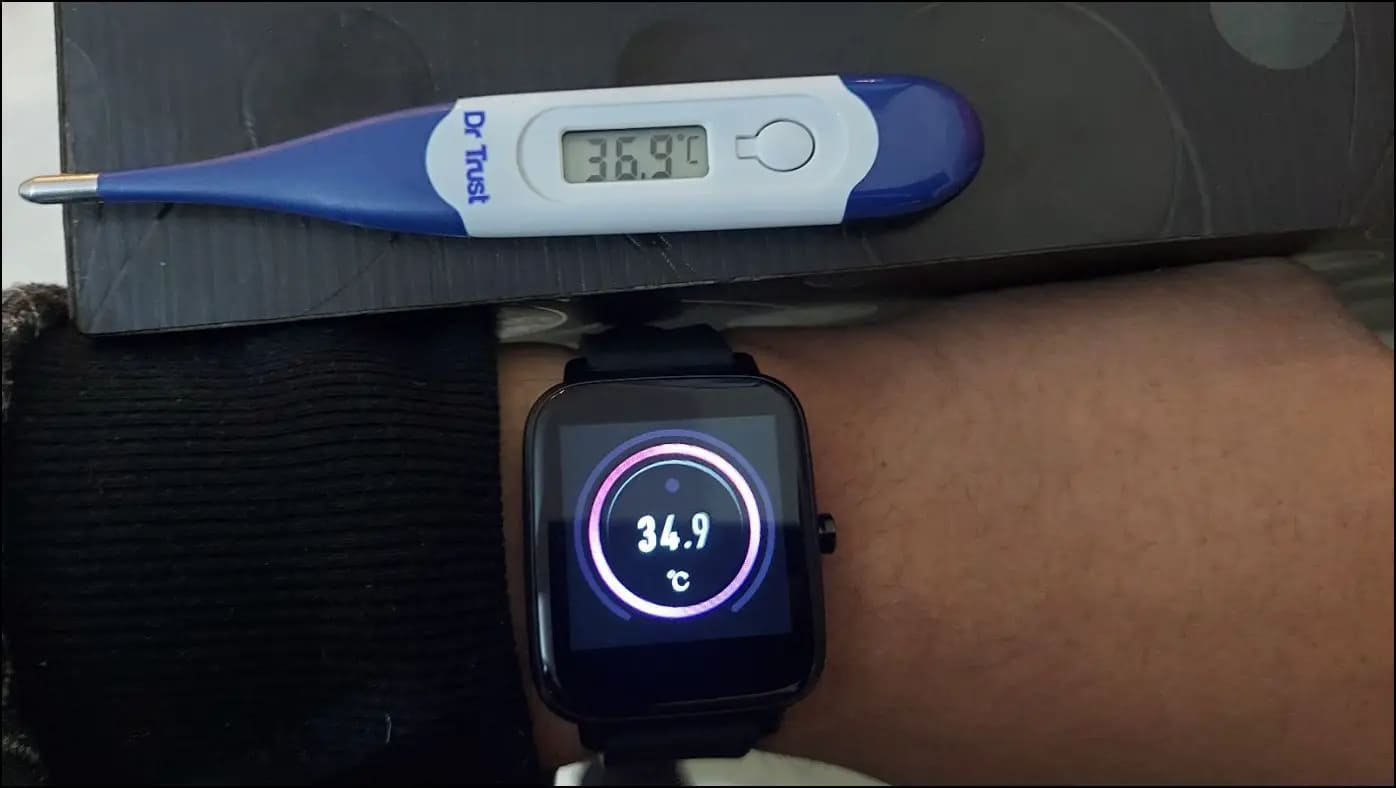
5. Body Temperature Sensor
A body temperature sensor on a smartwatch is used to measure your skin temperature. This is used to detect any slight change in your temperature. This can provide information on whether you are on the verge of catching a fever. These sensors can also help detect menstrual cycles as well.
Smartwatches with temperature sensors can only measure the skin’s temperature at the moment. Their ability to determine internal body temperature is still limited. Even with skin temperatures, external factors can affect the readings.
Since this is a recent addition to budget smartwatches, most generic brands and OEMs take advantage of it by including a fake temperature sensor.
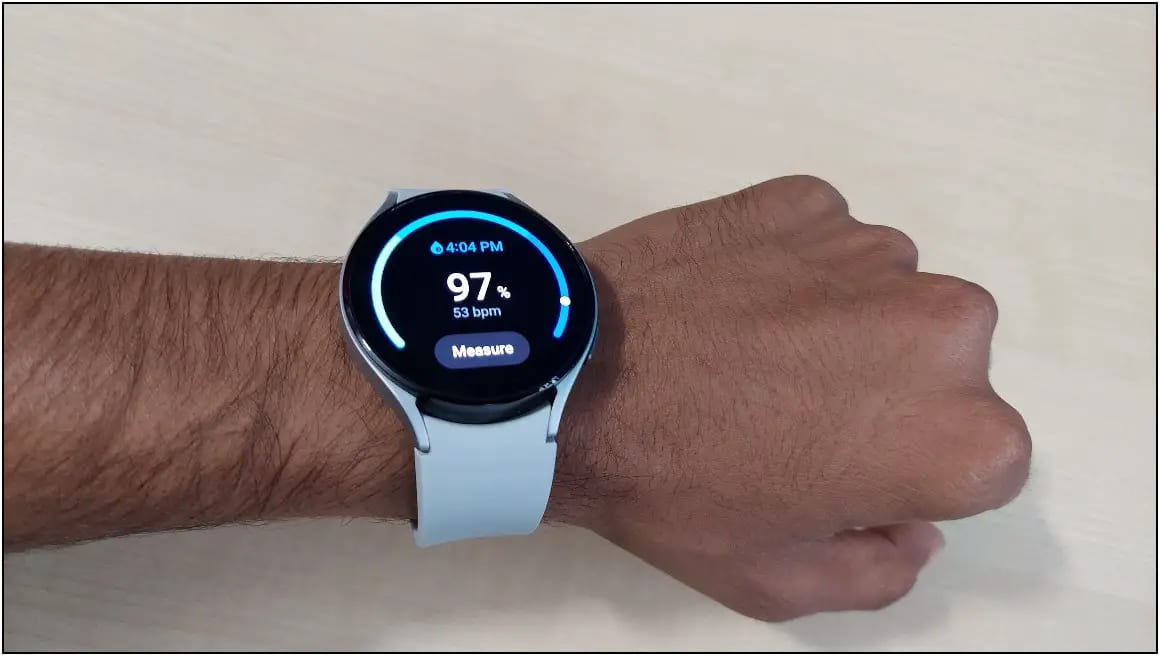
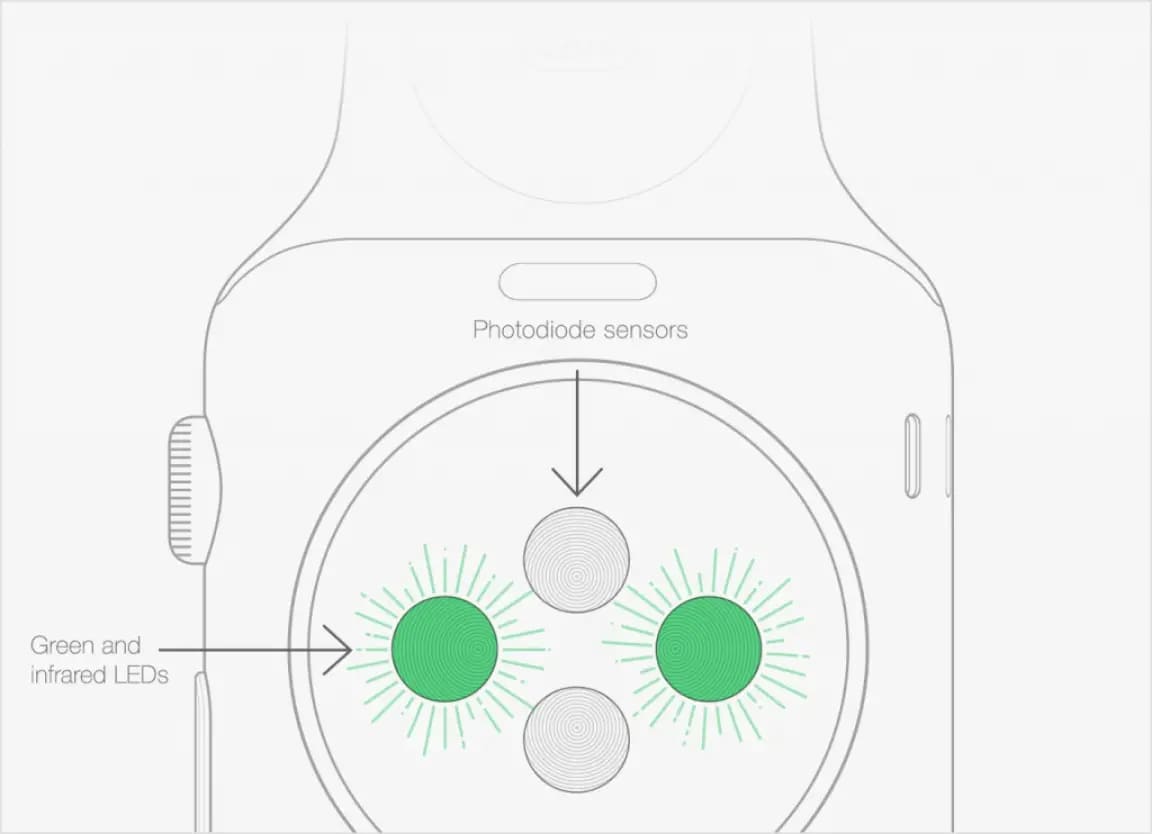
6. Heart Rate Monitor
Heart rate monitors are key reasons why smartwatches sell like hotcakes. As the name goes, it helps detect pulse rate. Most smartwatches use photoplethysmography (PGP) sensors for the same. Here’s a simple explanation of how it works:
Greenlight is strongly absorbed by red – the color of our blood. As your pulse causes a rhythmic change in the amount of blood, there is a change in the redness of your skin, too. Therefore, the green light detects the changes in the blood by measuring the amount of light reflected. This is how your pulse rate is detected.
Of course, the top-of-the-line smartwatches have a great amount of accuracy, but they aren’t as accurate as any chest-worn heart monitors.
Devices like Apple Watch detect anything unusual with your heart health by identifying low/high heart rates or irregular heart rhythms. It only provides you with information but does not provide any inferences, as it suggests you visit a medical professional.
7. Oximetry Sensor
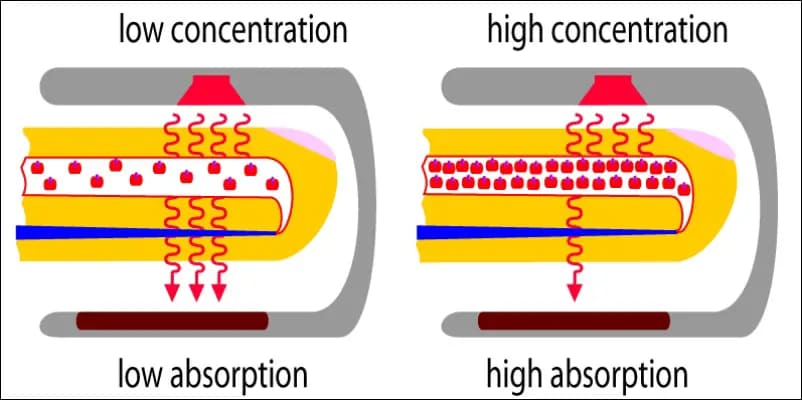
If there was one medical device found in most households, although deemed essential during very unfortunate times of the pandemic – it is the pulse oximeter. These sensors help you understand the Oxygen concentration in your blood through your smartwatch.
Hemoglobin is the protein present in your red blood cells that carries oxygen. We have something called saturated hemoglobin (full of oxygen) and unsaturated hemoglobin (lack of oxygen; not full). Both of them absorb different amounts of red light.
When your watch is tied to your wrist, it puts visible red and infrared light through your skin. Now, the light absorption ratio from the two ‘types’ of hemoglobin is measured and compared. Thus, this ratio comparison can help identify how much of the hemoglobin in your blood is saturated and how much is not.
But, we highly recommend you keep a medically certified pulse oximeter with you as well and not solely rely on the ones provided by a smartwatch, especially in situations that need medical attention.
8. Ambient Light Sensor
Just like your smartphones, smartwatches include ambient light sensors to adjust the display’s brightness automatically. This sensor detects the surrounding light to adjust the brightness of your screen to the right amount.
This also helps conserve the battery on your device. But mainly, this sensor prevents your screen from stinging on the light toward your eyes when you are in darker environments! Moto 360 was the first Wear smartwatch to feature an ambient light sensor.
9. Altimeter Sensor
The altimeter sensor helps you detect any changes in height. This mainly includes the user climbing stairs or descending a slope. This sensor can also help detect any elevation change while running, as it significantly improves the calorie burn rate.
Sensors like these ensure that just the basic data like distance, speed, and direction are calculated but bring finer details like the elevation data.
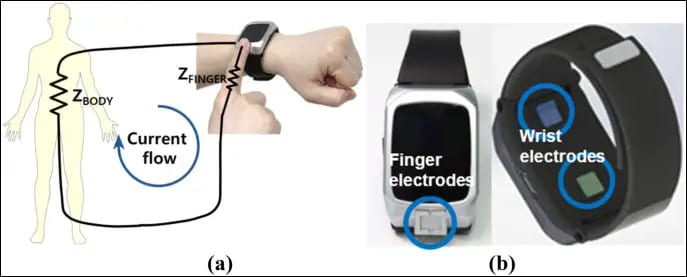
10. Bioimpedance sensor
A bioimpedance sensor measures the resistance being offered by the skin toward all amounts of electricity. The small amounts of current are delivered to the skin by the battery charging electrodes on the bottom face of your watch.
These measurements, driven by these currents, are used to measure sleep, heart rate, and respiration data. If you are notified that you have been inactive or lethargic, blame the bioimpedance sensor. And if the watch also comes with a water reminder feature, it is possible only because of the bioimpedance sensor.
For those unaware, the Samsung Galaxy Watch 4 comes with a BIA sensor which aids in measuring blood pressure, irregular heart rhythm (AFib), blood oxygen, and body composition.
11. Proximity Sensor
Proximity sensors let your watch know if you are using the device in the first place or not. They can detect an object or your hand without touching it from a distance.
If you are not using the device, this sensor helps save the battery and puts the watch to sleep. This sensor is also used to turn off or turn on the screen. Some gestures like waving to accept or reject calls, turning off the screen, and similar ones use the proximity sensor on your smartwatch.
12. Orientation Sensor
An orientation sensor mainly detects the orientation of the device. This is quite a basic sensor, as it helps ensure you wear your smartwatch in the right direction. If not, this sensor helps correct the display contents automatically concerning the orientation.
13. Pedometer
The most basic sensor that’s present on every single wearable device – is the pedometer. The pedometer uses the accelerometer data to count the number of steps walked by the user and thus provides the step count at the end of each day.
A 10,10,000-steps is often considered a healthy practice for any individual, and the pedometer can help ensure you do so!
14. Calorie Counter
A calorie counter is a secondary component on your smartwatch that uses the movements of the body detected by the accelerometer. Calorie data is quite essential to stay aware of how effective your activities are.
This is largely beneficial in weight management or in selecting the most efficient activities for the same. Some of the companion apps for these smartwatches let you set a weight goal and primarily use the calorie data to keep you motivated and stay aligned towards your goal!
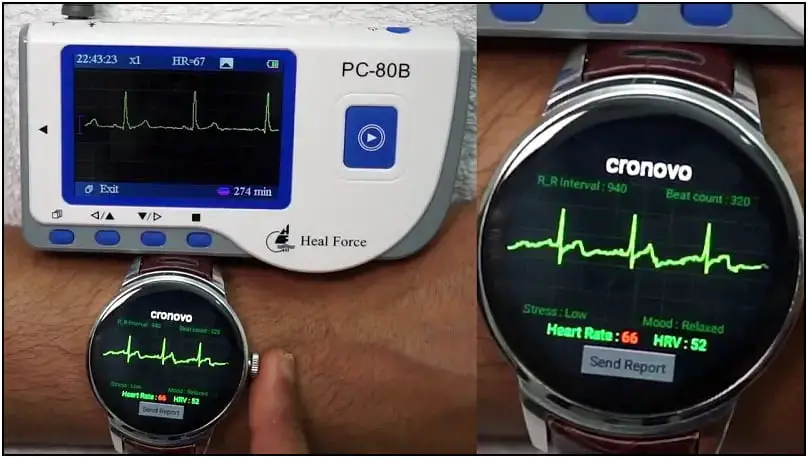
15. ECG Sensor
An ECG or electrocardiogram is a simple test to check your heart’s rhythm and electrical activity. The test results can provide information if there is a possible heart problem. These problems include chest pain, coronary artery disease, or a possible heart attack.
When you place your fingertip on the electrode, it creates a close circuit from the finger to the heart and then the wrist. This closed circuit allows your watch to record all the electrical impulses that make your heartbeat. The ECG sensor is a key selling point of the Apple watch.
The information from an ECG sensor can be quite important, and a person ideally has to take immediate medical assistance. Therefore, to avoid any false alarms, the ECG sensor on the Apple Watch checks the irregularity multiple times for data consistency.
The only disadvantage is that smartwatches with ECG sensors are expensive, and you probably have to shell out more! Popular smartwatches with ECG include Apple Watch Series 7, Samsung Galaxy Watch 4, and Fitbit Charge 5 and Sense.
16. Gesture Sensor
Smartwatches also pack a few nifty features like detecting gestures to control music playback and accept or reject calls. This is possible due to the presence of gesture sensors on your smartwatch. A few smartwatches also provide the option of adding custom gesture controls, which is also possible using the Gesture sensor.
17. UV Sensor
Some smartwatches also help you detect whether the sunlight you are exposed to is harmful or not.
These sensors mainly have light-sensitive elements called photodiodes. When light is incident on the sensor, the photodiode excites the electrons, causing an electric current. The electric current response is directly proportional to the strength of the light.
18. Electrodermal Activity Sensor (EDA)
An EDA (electrodermal activity) sensor is the most recent addition to Fitbit smartwatches. It helps you measure stress by combining the data from ECG, Skin Temperature, and heart rate sensors. Some smartwatches also factor in the sleep data.
It detects small amounts of electrical changes in the sweat level of your skin and thus helps you be aware of your stress levels. Thus, the electrical current is detected and then transformed into a digital output.
19. Skin Conductance Sensor
The skin conductance sensor helps calculate something called galvanic skin response – which mainly detects development that can be seen in your sweat, helping you stay aware of your emotional stress levels. It is also used to count the number of calories burned throughout the day.
These sensors detect the transformation within the sweat glands, as the electrodes in your watch are quite sensitive to these transformations on your skin.
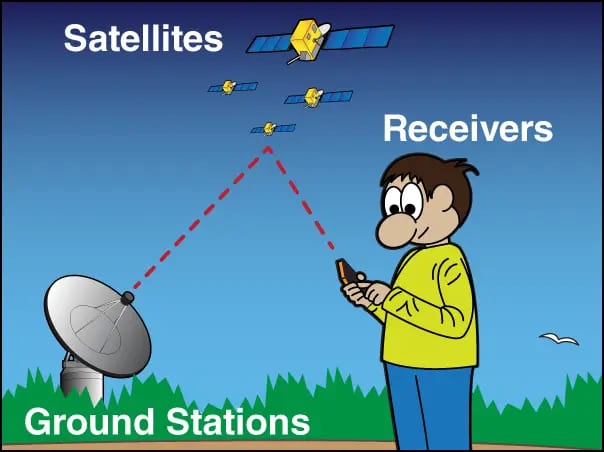
20. GPS Sensor in Smartwatch
GPS sensors these days are being made available on smartwatches as well. Like on your phones, this helps you provide direction and measure distance in your activities. A smartwatch’s ability to independently provide navigation data is quite a convenience for a lot of people.
If you have a GPS smartwatch, you can track and map your route, distance traveled, and speed while doing any activity, such as running, walking, cycling, climbing, and so on. It can also help determine elevation while hiking or trekking.
Some smartwatches use an altimeter to measure pressure changes at various heights to provide real-time elevation changes and accurately track the position. You also have the option of creating a three-dimensional map of your route.
Wrapping Up
These are the twenty most common sensors inside a smartwatch. We hope you found this article to be insightful and interesting. Do visit all of our related and more detailed articles linked above to learn more about sensors. Stay tuned to never miss an update in the world of wearable tech.