Quick Answer
- It is a much-awaited upgrade of the Ethereum blockchain network that will introduce several improvements to add blocks faster, reduce network congestion and gas fee, and shift to a proof of stake consensus mechanism.
- Sharding will help increase the scalability of the blockchain by adding 63 more chains making a total of 64 which will drastically reduce the load by splitting it among 64 chains running independently and side by side with the main blockchain.
- 0, let us take a closer look at the features and improvements that have been added at the time of writing this article or will be added soon.
You must have heard about Ethereum. It is the second-largest cryptocurrency after Bitcoin and one of the biggest blockchain networks in the world. But lately, it has been transitioning into a second phase called Ethereum 2.0. So you must be curious about it. In this article, we will discuss Ethereum 2.0, what improvements and changes it brings, and answer some of your FAQs to help you understand it better.
What is Ethereum 2.0?
Ethereum blockchain has seen widespread success and garnered millions of users. But it has been difficult to keep up with the demand. Currently, Ethereum can only add 15-30 blocks per second which often causes network congestion and leads to higher gas fees.
Ethereum 2.0, or Eth2 aims to solve all these issues. It is a much-awaited upgrade of the Ethereum blockchain network that will introduce several improvements to add blocks faster, reduce network congestion and gas fee, and shift to a proof of stake consensus mechanism. All these changes will make the Ethereum blockchain faster, more scalable, and more secure. Ethereum 2.0 is now officially called the Consensus layer.
Features and Improvements of Ethereum 2.0
To better understand Ethereum 2.0, let us take a closer look at the features and improvements that have been added at the time of writing this article or will be added soon.
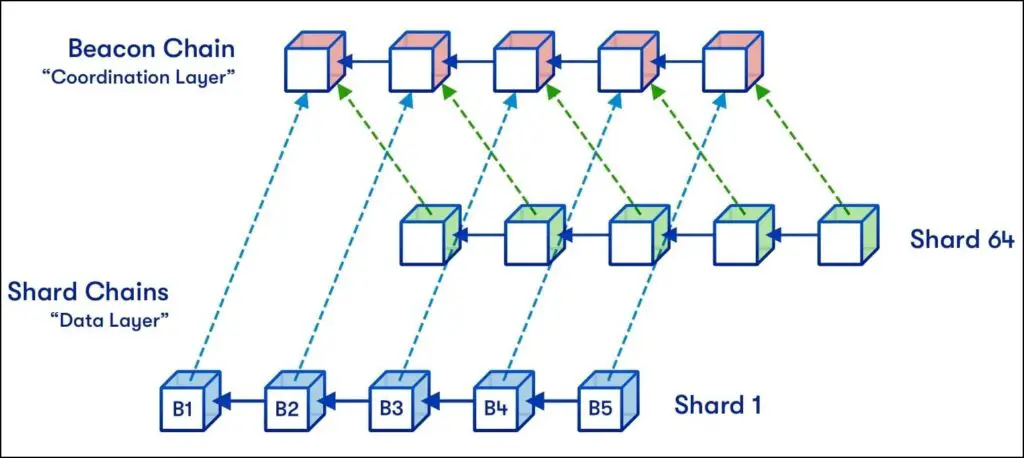
Beacon Chain
This was the first step in the roadmap of Ethereum 2.0, also known as phase 0 of the upgrade process. It is a separate mega blockchain running parallel to the Ethereum mainnet and uses a proof of stake mechanism. It was released on December 1st, 2020. In the upcoming phases, it will be merged with the Ethereum blockchain.
It will help in selecting winners of proof of stake who will validate transactions and manage or coordinate the expanded network of shards which we will discuss later. It will not handle transactions, accounts, and smart contracts.
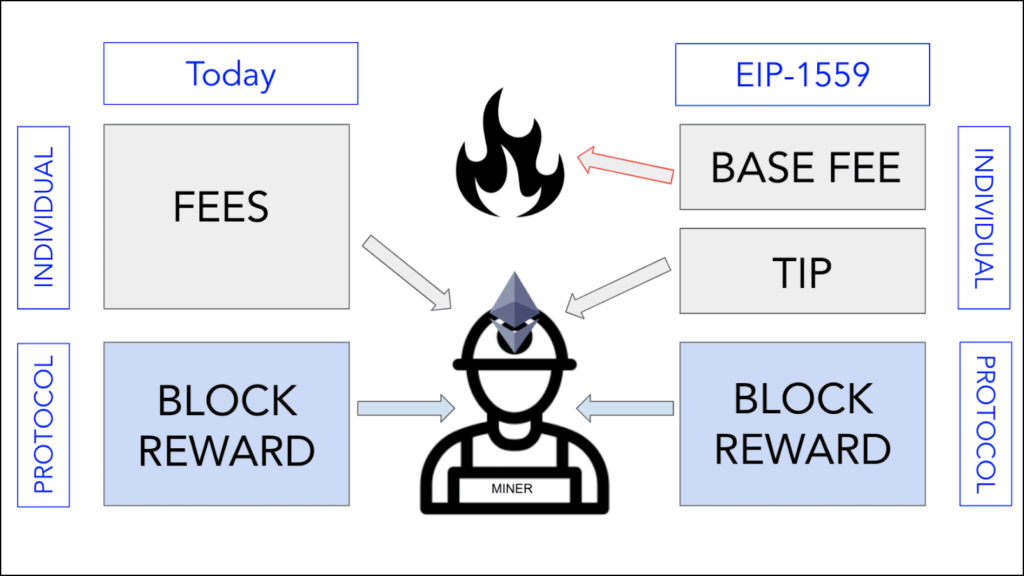
EIP 1559
EIP stands for Ethereum Improvements Proposal which is a standard for new proposals and features added. With EIP 1559, major changes were introduced to the controversial gas fee model of Ethereum. It proposes three tiers for the gas fee or transaction fee that is used to validate transactions. We will take a look at them one by one.
Base Tier
The base fee is set by Ethereum and is the minimum fee to add your transaction into a block. This fee will fluctuate based on traffic but should not exceed 20 gwei.
But all the fees collected from this base tier will be burned. This will add a deflationary factor to Ether which has been an inflationary coin due to its unlimited supply.
Priority Tier
Priority tier is a tip that you will give to the miner to process your transaction faster. This will be set by the user and will start from 2 gwei. The higher the fees, the faster your transaction will likely be processed.
Max fee
This is the final tier. Currently, whales or users with heavy pockets can overbid the gas price. The max tier will return the extra money to the user getting rid of the overbidding issue and making gas fees accessible for everyone.
Sharding Chains
Ethereum currently runs all its operations on a single chain. This will eventually require a lot of space and only powerful systems will be only able to validate transactions. This is one of the reasons that there is traffic congestion so often.
Sharding will help increase the scalability of the blockchain by adding 63 more chains making a total of 64 which will drastically reduce the load by splitting it among 64 chains running independently and side by side with the main blockchain.
Proof Of Stake
This is one of the key highlight features of the entire upgrade and is currently being tested on the Beacon chain discussed above. Ethereum has been using the proof of work method which is extremely resource-intensive, costs a lot of money for miners to operate, and wastes huge amounts of electricity.
The proof of stake consensus method will help fix all the above issues. Here, miners stake a certain amount of their coins and one miner is selected at random to process the transaction saving time, effort, and energy. Think of it as a roulette. Miners can stake more coins to increase their chances of getting selected. It is a consensus method that is used by several blockchains these days.
FAQs related to Ethereum 2.0
Q. When will Ethereum 2.0 be released?
Ethereum 2.0 is not a completely new blockchain but an upgrade to the current one. Features are slowly added and tested. It is being released over multiple phases. Here is a detailed list of all the phases and their expected release period:
Phase 0: Introduced beacon chain and a Proof Of Stake algorithm which is energy efficient. It was released on December 1st, 2020.
Phase 1: This phase will introduce 63 new chains and introduce Sharding. The expected release date was early 2022.
Phase 1.5: Merging of the Ethereum mainnet with the Beacon chain in a process called Docking. This phase will see the end of Ethereum 1.0 and the proof of work method. This is set to happen sometime in 2022.
Phase 2: This will include the launch and general bug fixes. It will also add some new improvements to the Ethereum virtual machine that runs its code. This will take place sometime after phase 1.5
Q. What is the Difference between Proof Of Work and Proof of Stake?
Proof Of Work: In Proof of work, several computers compete in a race to solve complicated problems and the winner gets to add a block to the blockchain and earn the mining rewards. But the resources of the rest of the computers go to waste. It consumes a lot of electricity and also costs a lot of money to operate such powerful computers.
Proof Of Stake: In Proof of stake, miners will stake their coins, and one of them will be selected randomly to add a block and earn rewards. Their chances of being selected will increase based on how much Ether they put at stake. This helps save a lot of electricity.
Q. Will Ethereum 2.0 reduce gas fees?
With the introduction of EIP 1559, users will have to pay a base minimum gas fee that is set by Ethereum that will not exceed 20 gwei and this fee will be burned completely. Users can then decide to pay a priority fee to the miner starting from 2 gwei to process their transaction faster. But anything over that will be returned to the user. This will help reduce the gas fee and also discourage overbidding.
Q. Is Ethereum 2.0 replacing Ethereum?
No, Ethereum 2.0 is just a network upgrade to the Ethereum we all know. It is not a new blockchain. To avoid this ongoing confusion, the developers of Ethereum have officially started calling it The Consensus layer.
Q. Will Ethereum become deflationary?
It is possible that under the proof of stake system, Ethereum may go deflationary. Right now, there is no cap on Eth but with the introduction of EIP 1559 where the gas fee is proposed to be burned, there is a possibility that more efforts will be taken to make Ethereum deflationary.
Wrapping Up
Ethereum 2.0 is set to bring some awaited improvements to the blockchain. This will hopefully help fix all the current persisting issues and give Ethereum a new life and attract more users. But there is still a lingering question of when it will happen, as the idea was proposed to take place in 2019 but did not start until 2020. We hope to see Ethereum 2.0 in full effect soon.
You can also follow us for instant tech news at Google News or for tips and tricks, smartphones & gadgets reviews, join GadgetsToUse Telegram Group or for the latest review videos subscribe GadgetsToUse Youtube Channel.